Physic-informed learn to design proteins
Physic-informed learn to design proteins (PhiGDesign). The residue communities, as important evolutionary signatures, would pave a way to engineer protiens for drug development.
How to use PhiGDesign
Single mutagenesis
Complete single mutagenesis. The matrix that is computed by the SAEC method shows \(\Delta E\) — the energy difference of each mutant sequence with each mutation \(\tau\) at the ith site and wild-type (WT) sequence, negative values representing favourable while positive representing unfavourable mutations.

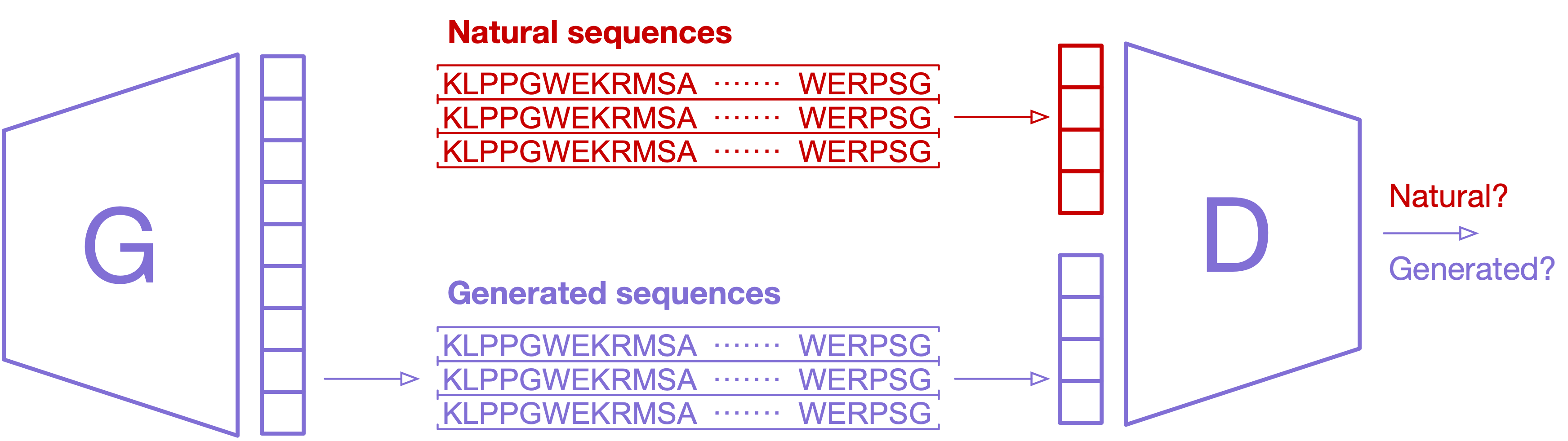
Sequence design

Starting from a given WT sequence, we launch the dead-end elimination (DEE) algorithm1 to optimize the mutant sequence base on the energy-like potentials (sequence potentials) inferred from the MSA. According to the Metropolis criterion, the design protocol will accept or reject a new mutant that may occur in the WT sequence, and the change is accepted with probability as follows,
\(P=\min\{1, e^{-\Delta E/kT}\}\)
where \(\Delta E=E_{new}-E_{old}\) is the energy difference between the new and old mutant sequences, \(k\) is the Boltzmann constant, and \(T\) is the temperature.
Coupled mutations
Based on the best-so-far sequence (designed), one can conduct a signle or multiple (coupled) mutants on the WT sequence, and the energy of the mutant sequence is computed for evaluating the conbination of mutants.
References
- [1] N. J. Cheung, et al., Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 19, 3556–3563 (2022)
- [2] N. J. Cheung,W. Yu, BMC bioinformatics, 20, 1–11 (2019)
- [3] J. Desmet, M. D. Maeyer, I Lasters, Nature, 356(6369):539-42, (1992)