- Lipid transport
Lipid Transport
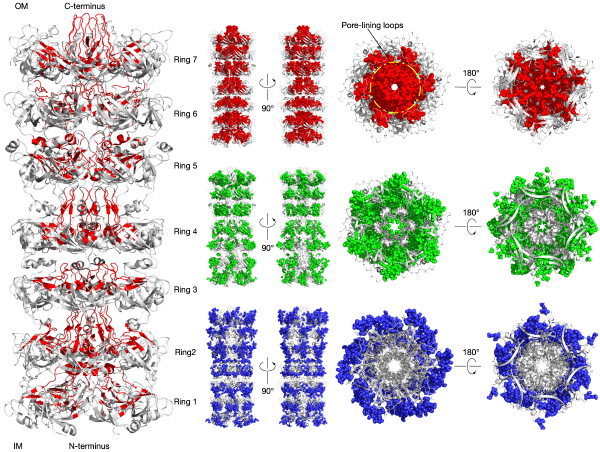
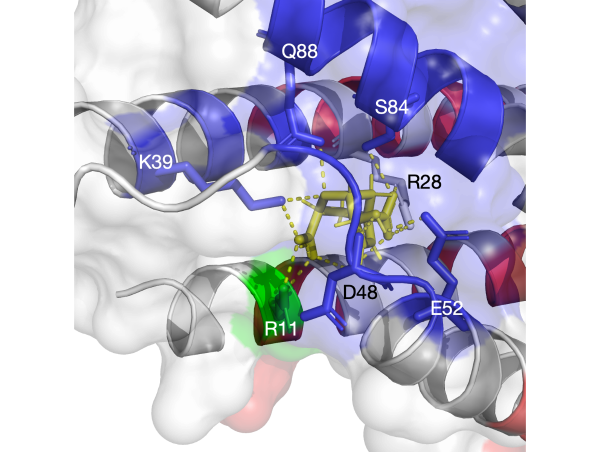
Most lipids are from the endoplasmic reticulum to import into mitochondria, and the transportation requires interaction of the two organelles.
Work on computational biology with a minor in biophysics, develop computational tools for protein folding & engineering and now work on statistical methods to address the molecular mechanisms of lipid exchange at membrane contact sites and interpret how the genetic variations impact the lipid transport and biosynthesis applications.



Known as : N. J. Cheung
Phone : +44-(0)75 123 13219
Expertise : Bioinformatics
E-mail : yaan.jang[AT]gmail.com
Work involves molecular mechanisms of lipid exchange at membrane contact sites, lipid transporters, protein engineering, folding pathways & structure prediction, GPCR-G protein binding & signalling, data analysis & modeling, sequencing data analysis, machine learning, Bayesian statistics
Coding Lines
Projects Done
Talks
Visiting
I am also interested in the application of machine learning and optimization algorithms to protein design, folding and its tertiary structure prediction. These include Boltzmann machine, deep neural networks, Bayesian optimization algorithms, and swarm intelligence. I am developing SENET (a sequentially evolving framework) that can be used in structural informatics and to aid molecular design
Deep Learning & OptimizationBroadly, I'm interested in developing computational methods that can be leveraged in design of biological molecules for practical applications. Especially, I work on designing proteins that bind with high affinity & specificiy to target mollecules and are used for therapeutics, creating catalysts for chemical reactions via enzyme design, and developing sampling algorithms & forcefields for validating the designs
Protein Folding & DesignI leverage Amo and SATAY (in silico) to study the molecular mechanisms of lipid exchange at membrane contact sites and how the transporters devliver the lipids between mitochondria and ER, as well as other organelles. Being rooted in physical principles, identifying evolutionary signatures allows for residue-level interpretation of their roles in lipid transportation and inter-molecular interactions
Lipid Transport & Data AnlysisAmo (Amoai v2.7.5) is elegant with modular codes, efficient with high-performance, precise at high accuracy, and fast at high speed
SENET is a sequentially evolving framework and projected to build a learning engine for recognizing our life in a digital way
Sibe is a powerful biological engine and used for protein tertiary structure prediction, deep learning, statistical analysis, and optimization
MoDyFing is an approach for predicting protein folding pathways and tertiary structure from its primary sequence
An integrated approach for iteratively predicting protein folding pathways and tertiary structure from its primary sequence
OptiFel is a data-driven modeling method based on a heterogeneous particle swarm optimization (CHPSO) algorithm
©
10/2019 - present University of Oxford
Molecular mechanisms of lipid traffic at contact sites
Sequencing data analysis for SATAY
07/2018 - 09/2019 University of Cambridge
Machine learning and Bayesian inference
The sequentially evolving neural network framework
11/2016 - 05/2018 DGIST
Structural bioinformatics & fMRI data analysis
Developed Sibe for protein, brain and cognitive studies
2012 - 2016
2014-2016 The University of Chicago
2012-2014 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
©

©
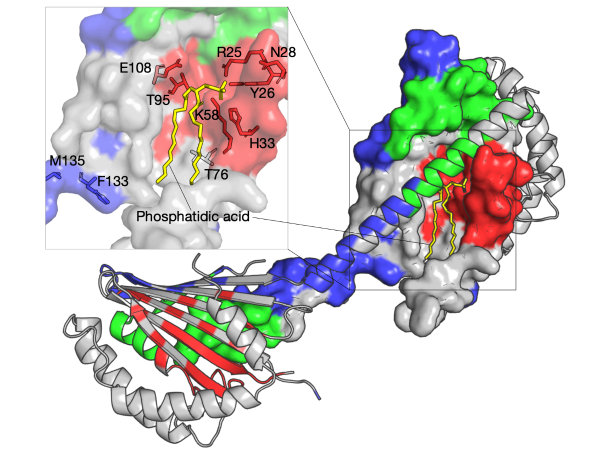
Most lipids are from the endoplasmic reticulum to import into mitochondria, and the transportation requires interaction of the two organelles.
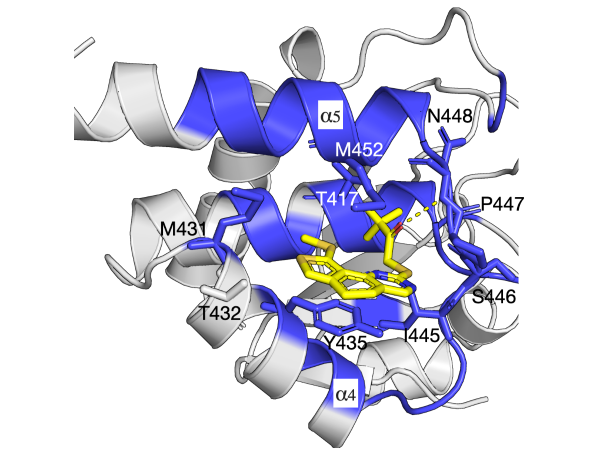
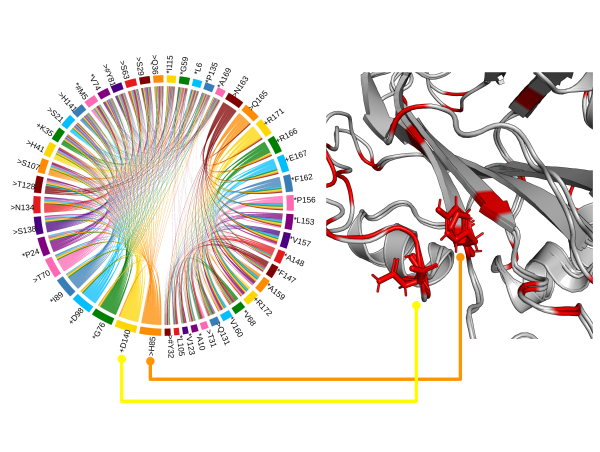
Proteins have highly ordered characterics at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels, and they also play important roles in protein functions.
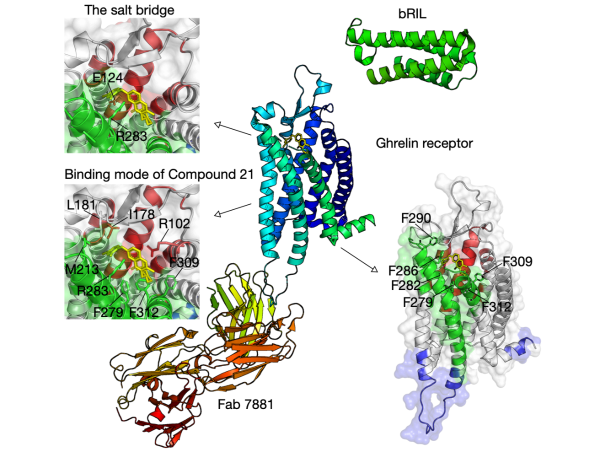
The selective coupling betwen GPCRs and specific G proteins plays critical role to produce appropriate intracellular responses.
Protein design has been a long-standing challenge to test our ground understanding in protein folding and structures.
Folding allows a protein to adopt its functional shape, and understanding the way proteins fold leads to a better analysis of molecular mechanisms.
Deep learning has a powerful ability in processing large numbers of features for understanding knowledge in the unstructured data.
©
©